Industrial tubing is crucial in various industries, serving as a conduit for fluids, gases, and other materials. Corrugated tubes stand out for their unique design and versatile applications among the many industrial tubing types. This blog will delve into the fascinating world of corrugated tube manufacturing, exploring the intricate process behind these vital components.
What Are Corrugated Tubes?
Corrugated tubes, or flexible metal hoses, are cylindrical conduits with a distinctive wavy or corrugated structure. This design imparts flexibility, making them ideal for applications requiring vibration absorption, thermal expansion, or the ability to navigate tight spaces. Corrugated tubes find use in automotive, aerospace, HVAC, and other industries.
The Manufacturing Process
The production of corrugated tubes is a precise and carefully controlled process that involves several stages. Let’s break down each step in the manufacturing journey:
Material Selection:
The process begins with selecting the appropriate material, typically stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant alloys. The material choice depends on the intended application, as different materials offer varying strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance levels.
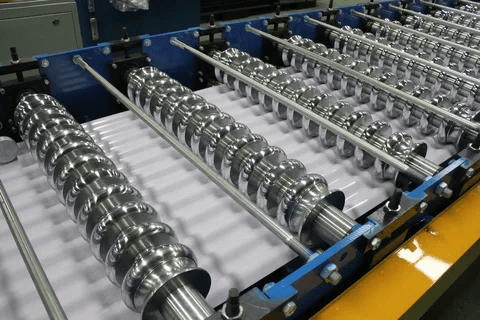
Tube Forming:
The selected material is fed into a machine that forms it into a continuous tube. This initial tube is typically smooth and cylindrical, devoid of the characteristic corrugations.
Corrugation:
Corrugation is the defining step in the process. A machine equipped with specialized rollers presses the smooth tube, creating distinctive wave-like corrugations. The spacing and depth of these grooves can be customized to meet specific requirements.
Welding:
In some cases, corrugated tubes may require additional fittings or connectors. Welding is used to attach these components to the tube, ensuring a secure and leak-free connection. Precision welding techniques are employed to maintain the tube’s structural integrity.
Quality Control:
Quality control is an integral part of the manufacturing process. Corrugated tubes undergo rigorous testing to meet industry strength, flexibility, and leak resistance standards. Common tests include pressure testing and X-ray inspection to detect any imperfections.
Surface Treatment:
Depending on the intended application, the corrugated tubes may undergo surface treatments such as passivation or coating to enhance corrosion resistance and improve longevity.
Packaging:
Once the tubes pass all quality checks and surface treatments, they are carefully packaged to prevent damage during transportation and storage. Proper labelling and documentation are essential for traceability and product identification.
Applications of Corrugated Tubes
Corrugated tubes are incredibly versatile and find application in a wide range of industries:
- Automotive: In the automotive industry, corrugated tubes are used for exhaust systems, fuel lines, and brake lines, where flexibility and resistance to vibration are essential.
- Aerospace: In aircraft and spacecraft, corrugated tubes are employed for various purposes, including conveying fuel, hydraulic fluids, and gases, thanks to their lightweight and flexible nature.
- HVAC Systems: Corrugated tubes are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to connect heating elements, boilers, and air handlers. Their flexibility allows for easy installation in tight spaces.
- Industrial Machinery: These tubes are essential in industrial machinery and manufacturing equipment, facilitating the safe transfer of gases, chemicals, and other fluids.
- Medical Devices: Corrugated tubes play a critical role in medical devices like endoscopes, where their flexibility and durability are crucial for precise and reliable performance.
Types of Corrugated Tubes
Standard Corrugated Tubes:
These are the most basic corrugated tubes, typically made from stainless steel or other metals. They feature a simple, evenly-spaced corrugation pattern and are used in various industries for applications such as conveying gases, liquids, and granular materials. They provide flexibility and strength while maintaining resistance to pressure and temperature variations.
Annular Corrugated Tubes:
Annular corrugated tubes have a spiral, spiral-like corrugation pattern, allowing for increased flexibility and axial movement while maintaining high pressure resistance. They are commonly used in applications where bending and twisting are frequent, such as in exhaust systems and flexible connectors.
Double-Walled Corrugated Tubes:
These tubes have two concentric corrugated layers with an insulating space between them. The double-wall design provides enhanced thermal insulation, making them suitable for applications where temperature control is critical. They are often used in HVAC systems and industrial heating processes.
Interlocked Corrugated Tubes:
Interlocked corrugated tubes have a unique design with interlocking ridges that provide excellent tensile strength and protection against abrasion. They are commonly used in cable protection applications, such as electrical wiring and cable conduits, where durability and flexibility are crucial.
Smooth Core Corrugated Tubes:
Smooth-core corrugated tubes have a corrugated outer layer but a smooth inner core. This design minimizes the risk of particle entrapment and allows for easy cleaning, making them suitable for food and pharmaceutical processing and for conveying abrasive materials.
Flexible PVC Corrugated Tubes:
These corrugated tubes are lightweight and highly flexible and made from flexible PVC (polyvinyl chloride). They are often used in residential and commercial applications for cable management, including organizing and protecting electrical and data cables.
Plastic Corrugated Tubes:
These tubes are typically made from polyethene (PE) or polypropylene (PP). They are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and suitable for various applications, including drainage systems, automotive wiring harnesses, and protective sleeves for hydraulic hoses.
Corrugated Metal Hose:
Corrugated metal hoses are flexible conduits made from stainless steel or other metals. They are used in applications that require high-pressure resistance and temperature tolerance, such as in the petrochemical, pharmaceutical, and aerospace industries.
Bellows Expansion Joints:
While not technically tubes, bellows expansion joints consist of multiple convolutions or corrugations, allowing axial, lateral, and angular movement. They primarily absorb vibrations and compensate for thermal expansion and contraction in pipelines and industrial equipment.
Custom Corrugated Tubes:
Manufacturers can create custom corrugated tubes with specific corrugation patterns, materials, and dimensions to meet unique industrial requirements. These tubes are tailored to the precise needs of the application, ensuring optimal performance.
Conclusion
Corrugated tube manufacturing is a meticulous process that produces highly adaptable and reliable components. These tubes are indispensable in various industries due to their unique design, flexibility, and resistance to harsh environments. As industrial tubing experts refine their manufacturing techniques, we expect to see even more innovative applications for corrugated tubes, contributing to the efficiency and reliability of countless systems across industries.

As the editor of the blog, She curate insightful content that sparks curiosity and fosters learning. With a passion for storytelling and a keen eye for detail, she strive to bring diverse perspectives and engaging narratives to readers, ensuring every piece informs, inspires, and enriches.